Any infectious diseases
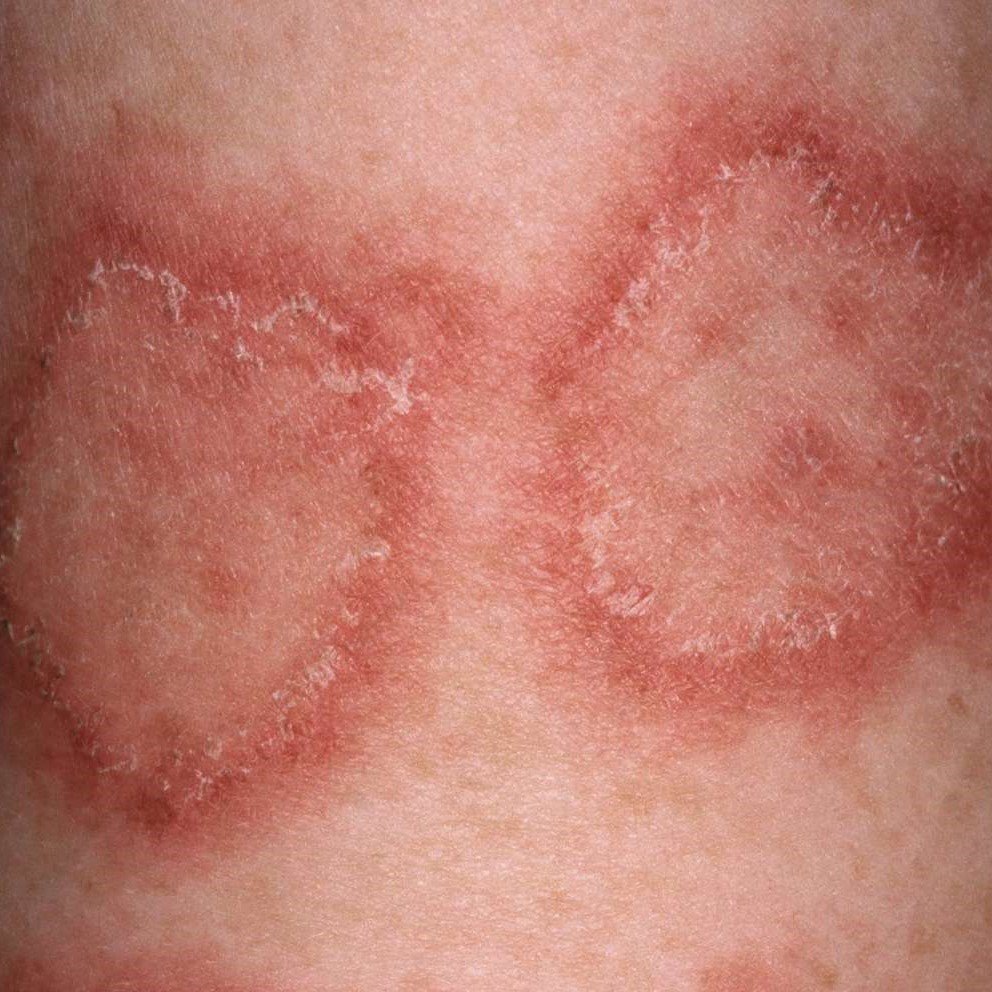
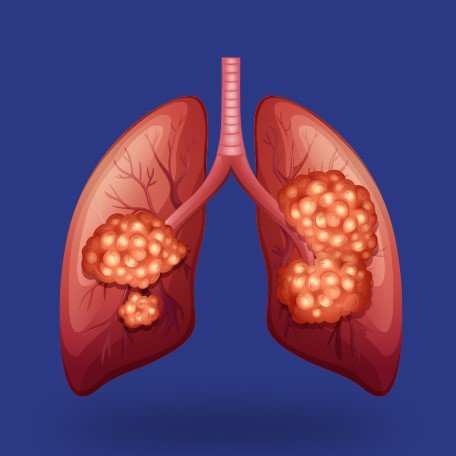
Infectious diseases are illnesses caused by pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites that can be transmitted from one individual to another or from the environment. Common examples include the flu, caused by influenza viruses, which can lead to symptoms like fever, cough, and body aches. Tuberculosis (TB) is a bacterial infection that primarily affects the lungs but can also impact other parts of the body, causing persistent cough and weight loss. Malaria, transmitted by mosquitoes carrying Plasmodium parasites, leads to fever, chills, and flu-like symptoms. HIV/AIDS, caused by the human immunodeficiency virus, progressively weakens the immune system, making individuals susceptible to various infections and diseases. These diseases can spread through various routes, including direct contact, airborne droplets, contaminated food or water, and vector-borne transmission. Effective prevention measures include vaccination, good hygiene practices, safe food handling, and vector control. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to manage and control the spread of infectious diseases.